AWS re:Invent has always been a bellwether for where cloud technology is headed. But in 2025, the signal was unusually clear: AWS is no longer just expanding its portfolio, it is reshaping how enterprise IT operations, cost management, and automation will function going forward.
Apiphani engineers attended AWS re:Invent 2025 to assess what these changes mean for enterprises running complex, mission-critical environments. Rather than cataloging product announcements, we focused on identifying the structural shifts behind them.
Four themes stood out.
1. AWS Is Moving from AI Tools to Autonomous Operations
Across re:Invent 2025, AWS demonstrated a decisive move beyond generative AI assistants toward agentic AI (autonomous agents capable of executing operational tasks across development, infrastructure, and security). Announcements such as Bedrock AgentCore, AWS DevOps and Security Agents, and autonomous software development agents all reinforced the same direction: AI is becoming an active participant in operations, not just an advisory layer.
This represents a meaningful shift for enterprise IT. Incident detection, root-cause analysis, and remediation are no longer envisioned as purely human-driven workflows. Instead, AWS is embedding operational intelligence directly into the platform (as is apiphani), with agents designed to persist, learn, and act across systems.
For enterprises, this challenges traditional support models built around tiered escalation, manual triage, and institutional knowledge concentrated in a small number of senior engineers. Over time, organizations that successfully operationalize autonomous capabilities should see fewer incidents, faster resolution, and less operational noise — while those that don’t may struggle to keep pace with growing system complexity.
2. Cost Optimization Is Becoming a Native Cloud Capability
Another clear emphasis at re:Invent 2025 was cost. AWS introduced new Database Savings Plans, AI-driven cost forecasting, and expanded automation across storage tiering and resource optimization. Collectively, these announcements signal that AWS is moving cost management closer to the infrastructure and runtime layers of the platform.
The implication is significant: cost optimization is no longer positioned as a separate FinOps function or a retrospective reporting exercise. Instead, it is becoming a real-time architectural and operational concern, informed by usage patterns, system behavior, and predictive models.
For enterprise IT leaders, this increases the need for tighter alignment between finance, architecture, and operations. As environments become more automated and dynamic, manual cost controls and disconnected tooling will become increasingly ineffective. The organizations that succeed will be those that design cost awareness directly into how systems are built and operated.
3. Serverless and Traditional Compute Are Converging
AWS also continued to blur the line between serverless and traditional compute. Enhancements such as Lambda Durable Functions, Lambda Managed Instances, and next-generation Graviton processors point toward a convergence of execution models.
Long-running, stateful workloads can now leverage serverless patterns without sacrificing predictability or performance. At the same time, AWS is assuming more responsibility for availability, scaling, and infrastructure management.
For enterprises, this changes the nature of architectural decisions. The question is no longer simply “serverless versus servers,” but where operational responsibility should live, with application teams, internal platform teams, or the cloud provider itself.
This convergence creates opportunities to reduce operational overhead, but it also raises the bar for design discipline. Poorly architected applications will surface performance and cost issues faster than ever in highly automated environments.
4. Regulated and Hybrid Environments Are Now First-Class Design Targets
Finally, AWS made it clear that regulated, sovereign, and hybrid environments are no longer edge cases. Announcements related to AWS AI Factories, expanded hybrid capabilities, and deeper governance and security integration signal a deliberate investment in supporting industries with strict compliance, residency, and operational control requirements.
This marks an important inflection point for enterprises that have delayed modernization due to regulatory constraints. AWS is signaling that hybrid and on-premises deployments are not temporary compromises; they are strategic architectures that will continue to evolve alongside public cloud services.
For regulated enterprises, the challenge will shift from whether modernization is possible to how automation and AI can be introduced responsibly without increasing operational or compliance risk. Success will depend less on technology adoption and more on operational maturity.
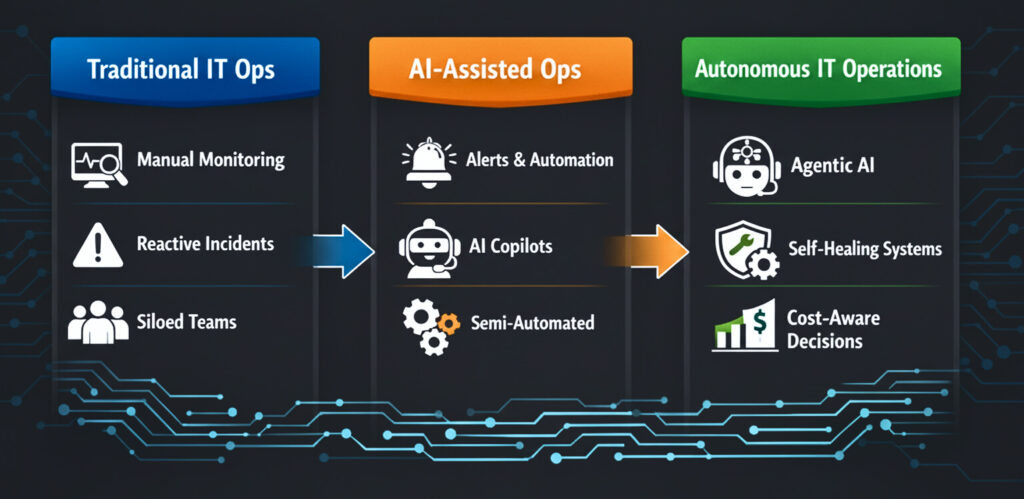
Evolution of Enterprise IT Operations
Looking Ahead
Across these themes, one message from AWS re:Invent 2025 was consistent: the future of enterprise IT is autonomous, cost-aware, and deeply embedded into the operational fabric of the platform.
The organizations that benefit most will NOT be those that adopt the most services, but those that can operationalize automation, governance, and cost control across complex, mission-critical environments intentionally and responsibly.
Contact Us
- Tell us more about your business and what you need from automation and business software.
- 53 State Street
Suite 505
Boston MA, 02109 - Request a Quote: +1 (833) 695-0811
